Pelvic health is a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of overall well-being. The pelvic region houses vital organs such as the bladder, reproductive organs, and bowels, playing a significant role in various bodily functions, including urinary control, sexual function, and bowel movements. However, issues affecting pelvic health, such as pelvic pain, incontinence, and pelvic organ prolapse, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore pelvic health solutions, from understanding common pelvic health issues to prevention strategies and management techniques.
Understanding Pelvic Health
The pelvis is a complex structure comprised of bones, muscles, ligaments, and organs that play integral roles in supporting bodily functions such as urinary control, reproductive health, and bowel movements. To grasp the significance of pelvic health, it’s crucial to understand the components and functions of this intricate region:
- Pelvic Floor Muscles: The pelvic floor muscles are a group of muscles that form a supportive hammock-like structure at the bottom of the pelvis. These muscles provide crucial support for the pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus, and rectum. Functionally, the pelvic floor muscles play key roles in maintaining urinary and bowel continence, supporting the pelvic organs against gravity, and facilitating sexual function. Weakness or dysfunction of the pelvic floor muscles can lead to pelvic organ prolapse, urinary or fecal incontinence, and pelvic pain.
- Pelvic Organs: The pelvic cavity houses several vital organs, including the bladder, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and rectum. Each of these organs performs distinct functions related to urinary, reproductive, and digestive health. For example, the bladder stores urine produced by the kidneys and expels it during urination, while the uterus plays a central role in menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth. Proper positioning and function of the pelvic organs are essential for overall pelvic health and function.
- Nerves and Blood Vessels: The pelvis is richly innervated with nerves and supplied with blood vessels that provide sensation, control, and nourishment to pelvic organs and muscles. Nerves in the pelvic region play critical roles in regulating bladder and bowel function, transmitting sensory information related to touch and pain, and facilitating sexual arousal and orgasm. Blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to pelvic tissues, supporting their function and repair. Damage or dysfunction of pelvic nerves and blood vessels can lead to symptoms such as pelvic pain, urinary or bowel dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction.
- Hormonal Influence: Hormones play a significant role in regulating pelvic health, particularly in women. Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause can impact pelvic organs and tissues, influencing bladder and bowel function, pelvic muscle tone, and vaginal lubrication. For example, estrogen levels decline during menopause, leading to changes in vaginal tissue elasticity and lubrication, which may contribute to symptoms such as vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse. Hormonal imbalances can also affect pelvic muscle function and contribute to conditions such as pelvic pain and incontinence.
- Psychological Factors: Psychological factors, including stress, anxiety, and past traumatic experiences, can influence pelvic health and function. Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and pelvic pain, exacerbate symptoms of urinary and bowel dysfunction, and impact sexual arousal and satisfaction. Additionally, past traumatic events such as sexual abuse or childbirth trauma can have long-lasting effects on pelvic health, leading to symptoms such as pelvic pain, sexual dysfunction, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Addressing psychological factors through counseling, stress management techniques, and relaxation exercises can be an essential component of holistic pelvic health care.
- Impact of Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and posture can significantly impact pelvic health. A sedentary lifestyle and poor posture can weaken pelvic floor muscles and contribute to pelvic organ prolapse, urinary and bowel dysfunction, and pelvic pain. Conversely, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture can support pelvic muscle strength and function. Similarly, dietary factors such as hydration, fiber intake, and caffeine and alcohol consumption can affect bladder and bowel function and influence pelvic health outcomes.
Common Pelvic Health Issues
Several factors can contribute to pelvic health issues, ranging from lifestyle factors to underlying medical conditions. Common pelvic health issues include:
- Pelvic Pain: Pelvic pain can manifest as discomfort, pressure, or sharp, stabbing sensations in the pelvic region. Causes of pelvic pain may include muscle tension, inflammation, nerve compression, or conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or interstitial cystitis.
- Urinary Incontinence: Urinary incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine, ranging from occasional leaks to complete bladder emptying. Types of urinary incontinence include stress incontinence (leakage during physical activity), urge incontinence (sudden, intense urge to urinate), and mixed incontinence (combination of stress and urge incontinence). Risk factors for urinary incontinence include childbirth, menopause, obesity, and certain medical conditions.
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when pelvic organs, such as the bladder, uterus, or rectum, descend or bulge into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic floor muscles and ligaments. Symptoms may include a sensation of pressure or fullness in the pelvis, urinary or bowel symptoms, and visible bulging in the vaginal area. Risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse include childbirth, aging, obesity, and chronic constipation.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Sexual dysfunction encompasses various issues that interfere with sexual desire, arousal, or satisfaction. Pelvic health conditions such as pelvic pain, incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, or psychological factors can contribute to sexual dysfunction in both men and women.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While pelvic health issues can be challenging, there are several strategies individuals can implement to promote pelvic health and manage symptoms effectively. These strategies encompass lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises, behavioral changes, and professional interventions aimed at improving pelvic muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. Let’s explore these strategies in more detail:
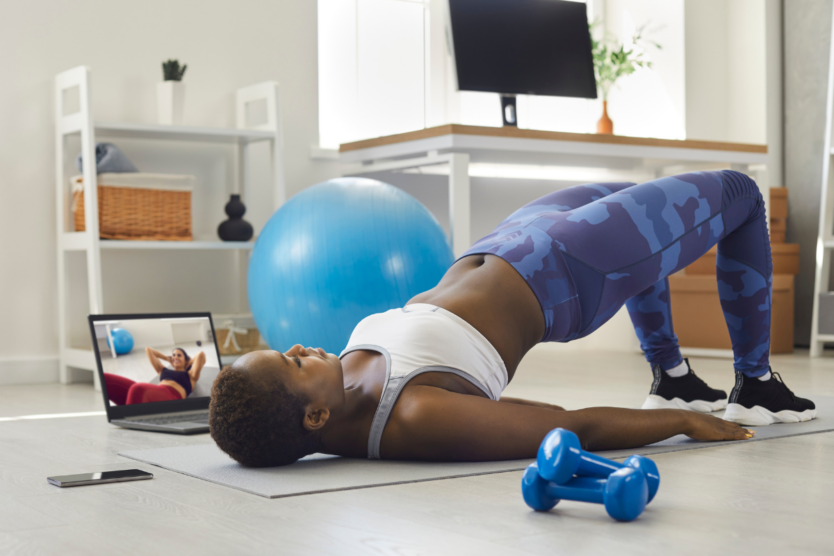
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Pelvic floor exercises, commonly known as Kegel exercises, are a cornerstone of pelvic health management. These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the muscles of the pelvic floor to improve strength and coordination. Regular practice of pelvic floor exercises can help individuals regain control over bladder and bowel function, reduce symptoms of incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse, and alleviate pelvic pain. Pelvic floor exercises can be performed discreetly at home and typically involve identifying and engaging the pelvic floor muscles, holding the contraction for a few seconds, and then relaxing. Consulting a pelvic health therapist or physical therapist specializing in pelvic floor rehabilitation can provide guidance on proper technique and progression of exercises. To be sure you’re doing Kegels properly, you can use a product like the INNOVO Urinary Incontinence Kit. These “smart shorts” are designed to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles from the inside out, allowing you to perform 180 perfect Kegels in 30 minutes. Subscribe to the INNOVO newsletter to receive a $20 discount code for your purchase!
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for promoting pelvic health and reducing the risk of pelvic health issues. This includes maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Obesity can increase pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, contributing to pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Eating a diet rich in fiber and staying hydrated can support digestive health and prevent constipation, which can strain the pelvic floor muscles. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help strengthen pelvic muscles and improve overall fitness.
- Bladder and Bowel Habits: Practicing good bladder and bowel habits can help prevent urinary and bowel dysfunction and reduce symptoms of pelvic health issues. This includes emptying the bladder regularly, avoiding delaying urination or rushing to empty the bladder, and avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption, which can irritate the bladder. Similarly, maintaining regular bowel habits, avoiding straining during bowel movements, and consuming a diet high in fiber can prevent constipation and reduce pressure on the pelvic floor muscles. Pelvic health therapists can provide guidance on bladder and bowel training techniques to improve bladder and bowel control.
- Pelvic Health Education: Educating oneself about pelvic anatomy, common pelvic health issues, and available treatment options is essential for proactive pelvic health management. Understanding the factors that contribute to pelvic health issues, such as childbirth, aging, and lifestyle habits, can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Resources such as books, online articles, and educational workshops can provide valuable information about pelvic health and treatment options. Additionally, healthcare providers, including pelvic health therapists and urogynecologists, can offer personalized guidance and support based on individual needs and goals.
- Pelvic Health Therapy: Pelvic health therapy, including pelvic floor physical therapy, is a specialized form of rehabilitation aimed at improving pelvic muscle function and reducing symptoms of pelvic health issues. Pelvic health therapists, typically physical therapists with additional training in pelvic floor rehabilitation, work closely with individuals to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs and goals. Treatment may include manual therapy techniques to release muscle tension, biofeedback to improve pelvic muscle awareness and coordination, and behavioral strategies to modify bladder and bowel habits. Pelvic health therapy can be highly effective in improving pelvic muscle strength, reducing symptoms of incontinence and pelvic pain, and enhancing overall quality of life.
- Medical Interventions: In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to manage pelvic health issues effectively. This may include medications to treat underlying conditions such as urinary tract infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, or hormonal imbalances. Surgical interventions may be recommended for severe cases of pelvic organ prolapse or other structural abnormalities contributing to pelvic health issues. It’s essential to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual needs and preferences.
See A Doctor
Use our Physician Finder to find a doctor near you with expertise in women’s health. Pelvic health is integral to overall well-being, yet it is often overlooked or misunderstood. By understanding the complexities of the pelvic region, recognizing common pelvic health issues, and implementing prevention and management strategies, you can take proactive steps to promote pelvic health and improve your quality of life. Whether through pelvic floor exercises, lifestyle modifications, or seeking professional pelvic health therapy, there are numerous pelvic health solutions available to support optimal pelvic health and function. Remember, prioritizing pelvic health is an investment in lifelong wellness and vitality.